Japan’s regulatory authority is among the list of regulatory authorities that are known to have strong regulatory requirements like the FDA or EU and is the reference authority for some countries. Similar to drugs and medical devices approval requirements, there are also requirements and standards put forward for cosmetics marketing in the country.
Given the highly competitive nature of the Japan cosmetics market, a thought that may cross is that Japan might have less strict cosmetic regulations. However, this is not true. Cosmetics in Japan are classified into 2 and the regulations differ for both. Continue to read to know more about Japan cosmetic regulations.
Highlights of the Cosmetic Market in Japan
- The Japanese cosmetics market ranks as the fourth-largest globally, comprising around 3000 companies and skincare being the most important one.
- The revenue in the cosmetic market is estimated to reach by US$7.92bn.
- An annual growth rate of 3.12% (CAGR 2025- 2030) is estimated.
Cosmetic Regulations in Japan
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) and the Pharmaceutical Medical Device Agency (PMDA) are the regulatory authorities that govern the cosmetic sector in Japan. Cosmetics are regulated under the Pharmaceutical and the Medical Devices Law. The applications made to the PMDA are forwarded to the MHLW in most cases and a decision is made. PMDA and MHLW therefore work together for the processing of applications for the licensing or approvals.
The Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) is an autonomous organization responsible for:
- Undertaking both on-site and document-based examinations to assess the safety and efficacy of quasi drugs and cosmetics.
- Assessing adverse effects associated with ingredients or products used in cosmetics.
- Reviewing applications submitted by importers and foreign manufacturers.
The general approval or registration process for cosmetics is given in the below image.
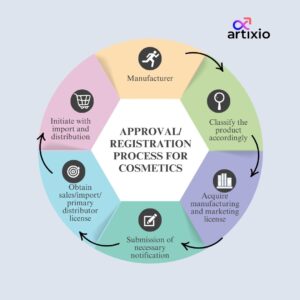
License Requirements For Cosmetics Products
The manufacturers/importers have to acquire for two licenses-
- Cosmetic manufacturing license (5 years validity)
- Cosmetic marketing license (5 years validity)
Foreign manufacturers (who wish to manufacture quasi drugs in foreign countries and import them into Japan) have to be ascribed by MHLW as an “Accredited Foreign Manufacturer”.
Prior to the application for accreditation, the marketing approval holder who must be Japanese will need to submit the Business Number Registration Form for obtaining a Business Number. The applicant must submit an Application for Accreditation to the Minister (in duplicate) and an Application for Accreditation Examination to the PMDA Chief executive. These applications must be submitted to the Administrative Division II of the PMDA’s Office of Review Administration.
Documents to be submitted are:
- A CV of the responsible person of the manufacturing establishment.
- The documents on manufacturing process and the list of products to be manufactured for importing into japan.
- Documents of the building and facilities of the manufacturing establishment.
- A document on the radiopharmaceutical type and an outline of the facilities handling them must be provided when radiopharmaceuticals are included.
- Copy of current valid license certificate issued by the governmental organization in the country where the foreign manufacturer resides given that if there exists a system for marketing licensing or approval, manufacturing license etc.
How Cosmetics are Labelled in Japan?
Labeling requirements are implemented according to Pharmaceutical Affairs Act-
Labelling of cosmetics is mandatorily expressed in Japanese language, outer packaging requires obligatory full ingredient list. Misleading or false expressions and unapproved claims with safety and efficacy effect in labeling is prohibited.
Quasi drugs which have claims should depend on the active ingredient in it and should be approved by MHLW. For the approval of quasi drugs MHLW allow for product effectiveness result that has to be recognized thus companies name them as medicated cosmetics.
Labeling items to be indicated on cosmetics are,
- Name of the product
- Name and address of the manufacturer or importer
- Brand name
- Quantity or weight of the product
- Manufacturing code or number
- Origin country
- Ingredient list designated by MHLW
- Any specific precautions on its storage and use
- Expiration date as designated by MHLW
- Contact information
Fee Applicable for Cosmetics in Japan
The fee varies according to the type of product that is being produced or imported. The fee structure for review of cosmetics is as follows:
| Cosmetic Type | Review Fee |
| Quasi-drugs | |
| New active ingredients | 3,10,100 Yen |
| New dosage form | 258,900 Yen |
| Others | 66,600 Yen |
| Cosmetics | 66,600 Yen |
**Please note that this might not be the exact or final fee. Kindly refer to the official website before proceeding with any payment**
What are Prohibited Claims in Advertisement?
A. Names other than names included in the PMDL Article 12, 18, and 22
B. If the scope is exceeded than given in the article 1,3 (3) of “ENFORCEMENT RULE OF PHARMACEUTICAL ACT”
C. Misleading or false claims related to safety, efficacy, ingredients, amount, and property of cosmetics and quasi drugs
D. Claims which cause the overconsumption and misuse of product
E. Claims which include “recommended by doctors, cosmetologists, etc.
F. The claims creating uncomfortable expressions.
Information provided above are some examples of prohibited claims in advertisements.
Notification Requirements
Before entering to market and selling the product the manufacturer/importers have to submit notification. This step can be done after obtaining cosmetic license.
Domestic manufacturer needs to submit only COSMETIC MARKETING NOTIFICATION to the same regulatory officials as granted the cosmetics marketing license. While foreign manufacturer has to submit COSMETICS (foreign manufacturer, importer) NOTIFICATION along with marketing notification.
Cosmetic and Quasi Drug Import
Manufacturer or importer are required to obtain PRIMARY DISTRIBUTOR’S LICENSE for cosmetics, this license is used for the renting, selling and lending of imported or manufactured cosmetics.
Any distributor engaging with the labeling, packaging and storage of imported or manufactured product has to obtain COSMETIC MANUFACTURING LICENSE (packaging, labelling and storage).
Documents required for Primary Distributor’s License are as follows:
- Corporate Registration copy (in case of corporation)
- Duty specifications list
- Medical certificate specifying the applicant
- Documents that certifies the qualification of a marketing supervisor -general along with their employment contract.
- Documents disclosing the quality management system and post marketing safety management system.
- Business facility and storage facility floor plan.
Documents required for Cosmetic Manufacturing License are as follows:
- Physical facility outline
- Manufacturing facility floor plan
- Documents that certifies the responsible engineer qualifications along with their employment contract.
- Testing laboratory contract copy (when applicable)
Additional Information About Japan Cosmetics Products
Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) Definition of Cosmetics in Japan
As per Article 2.3 of Pharmaceutical Affairs Law, the cosmetics are “Substances which possess mild actions and can be applied to human body by the source of sprinkling, rubbing or similar methods for the purpose of cleaning, increasing attractiveness, beautifying themselves and for altering the appearance for keeping the hairs and skin in good condition”.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) Categorization of Cosmetics in Japan
In Japan, cosmetics are categorized into two main groups:
- General Cosmetics
- Quasi Drugs
General Cosmetics: These are products that have mild actions when applied to the human body. They are meant for beautifying, cleaning or increasing the attractiveness which is to change the appearance or maintain good skin and hair by methods like sprinkling, rubbing or any other methods.
These products do not require a regulatory application for the market approval but have to be in compliance with the cosmetic product standards. They are divided into the following 6 categories:
General Cosmetic Categories
| General Cosmetic Categories | Examples |
| Perfume And Eau De Cologne | Eau De Colognes And Perfumes |
| Skin Care Cosmetics | Skin Milk, Cleansing Creams, Skin Lotion And Facial Creams |
| Makeup Cosmetics | Foundation Cream, Eye Makeup, Lipstick And Others |
| Hair Care Cosmetics | Shampoo, Hair Dyes, And Producs For Hair Treatments |
| Special Purpose Cosmetics | Shaving Cream, Sunscreen And Others |
| Cosmetic Soaps | Soaps For Cosmetics |
Quasi-Drugs: Quasi-drugs are products which are cosmetics with active ingredients that can have mild side effects to the human body when used. Clinical trials might be required to demonstrate the safety and efficacy. It is difficult to tell apart between the cosmetics and quasi drugs as this is based on the nature, variation in the effect, number of components used, application technique and appearance of the product.
It comprises of anti- acne creams, antimicrobial products, anti-sunburns, hair colour, straightening products, hair growth treatments, perm, deodorants, bath products, products for oily skin and to get rid of freckles, shaving creams, anti-dandruff shampoos etc.. are some of the products that are regulated as quasi- drugs.
How to Market Cosmetics in Japan?
The first step towards marketing a cosmetic product in Japan is the product ingredient analysis.
Analysis For Product Ingredients-
- Ingredient analysis is important before the registration of any cosmetics for the safety and efficacy of cosmetics or quasi drugs.
- The process of registration is same for both but the regulators and requirements may vary for cosmetics and quasi drugs.
- The manufacturers or importers have their own or contracted testing and inspection facilities which are designated by MHLW helps them to perform the ingredient analysis on product samples.
- Ingredient analysis can be done on heavy metals, harsh preservatives, legal colors and perfumes, UV protecting agents, etc. Some other basic tests such as microbial tests, pH, viscosity and stability tests.
There are certain ingredients which must be restricted for all types of cosmetics, some are restricted based on the type of the cosmetic product. The list of these ingredients are given in the MHLW Standards of Cosmetics.
Cosmetic Safety and Quality
Good Quality Practice(GQP) And Good Vigilance Practice (GVP)
The cosmetics to be marketed are properly assessed by the cosmetics production its safety and quality standards by the marketing license holders. They must have the systems which are capable for providing the report on consumer requirements and should have collection of information related to safety of products, examine the harmful effects of product and evaluates its safety and if license holder detect any kind of harmful effect in the product, they must report safety issue to MHLW. GQP and GVP is responsible for the safety control and marketing quality of cosmetics and quasi drugs.
Since cosmetics contain both chemicals and medicinal ingredients (Quasi- drugs), it is important to regulate them. This is done to ensure that the products entering into the Japan cosmetic market must not pose any threats to the public and must deliver its function as it is claimed to be. So, the MHLW and the PMDA strictly regulate cosmetics with a set of guidelines and mandatory requirements as they are responsible for the safety, quality and effectiveness of cosmetics including quasi drugs in Japan.
To make a product’s market entry, it is important to know the rules applicable to that country.
Here at Artixio, our regional experts can guide you through these rules and regulations. Our regional experts in Japan can assist you in document preparation, faster japanese cosmetic market entry, consultation with PMDA, local representation and more. Reach out through info@artixio.com
Frequently Asked Questions – Cosmetic Regulations in Japan
1. Who regulates cosmetics in Japan?
In Japan, cosmetics are regulated by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. This authority is responsible for formulating and implementation of regulations related to cosmetics.
2. What are Quasi drugs in Japan?
Products in Japan are categorized as either cosmetics or Quasi-drugs. These are the products somewhere in between cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. These drugs are labeled as such even if they appear to be essentially cosmetics.
3. How to import cosmetics to Japan?
To import cosmetics to Japan,
- Ensure that the products are in accordance with Law.
- Get the samples assessed according to the MHLW.
- Submit all the forms required and handle the clearance.
- Obtain cosmetic marketing notification.
4. What is the process to register cosmetics in Japan?
To register a cosmetic product in Japan,
- Complete Ingredient Analysis.
- Assign a responsible agent in Japan.
- Procure Marketing notification.
- Market cosmetics.
5. Who sets standards for cosmetic products in Japan?
In Japan, cosmetics are under the control of Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). It is the competent authority regulating cosmetics and formulating drug regulations and standards.
6. What is GVP?
As a part of the Good Quality Practices, marketing license holders are required to properly evaluate their production management and quality control of cosmetics to be marketed. Marketing license holders must establish systems that are capable of providing and retaining accurate information in response to consumer inquiries along with a monitoring system that handles customer complaints on product quality and product recalls, as required by the GVP standards.
7. What is GMP Inspection?
GMP compliance certificate is issued by the authorities after thorough inspection of the manufacturing sites. The compliance is issued only if all the requirements are met by the manufacturer.
8. Do cosmetics require regulatory approval to market it in Japan?
No, cosmetics do not require a market approval to market it in Japan. However, it must satisfy and comply with the Standards for Cosmetics.
9. What are some restrictions placed regarding the use of ingredients in cosmetics in Japan?
In Japan, it is prohibited to use any medical drug ingredients (exclusion for those only used as additives and those which are listed in Appendix 2-1 through 4). Also cosmetics must not include any ingredient which is not in compliance with Standard for Biological Materials.
10. How long does it take for the approval of a cosmetic (imported) for its marketing in Japan?
It takes approximately 6 months but this can be varied according to the complexity of the safety, quality and efficacy details of the product.
11. In which language should I submit my documents to the PMDA?
The documents submitted for the regulatory approval must be in Japanese. The entire text must be translated in case of translated documents and the original text before translation must also be provided. The name and affiliation of the translator along with the technical specialist who reviewed the content must be given.





